November 2, 2023: Dr. Sanford Nidich was invited to present at a Ukraine Medical Conference, Current Status of Personalized Medicine: Global Issues and Prospects for Research. The title of his talk: Effects of Transcendental Meditation on PTSD, Depression and Sleep Problems in Veterans, Military Personnel and Other High Risk Groups. At 9:15 into the video, Dr. Nidich makes a PowerPoint presentation covering some of the related scientific research on Transcendental Meditation (TM). I selected Transcript, copied his talk leading up to the PowerPoint, and added a few hyperlinks. The whole video presentation is 29:25 minutes.
Thank you very much for inviting me to speak to this very prestigious conference, Current status of Personalized Medicine: Global Issues and Prospects for Research. It’s very important that we look at alternative approaches, including personalized approaches to medicine. The field is changing very rapidly, and it’s changing for the better. We’re able to help people progress with their disorders. We’re able to talk about and apply preventative medicine much more readily in a more accepted way than ever before.
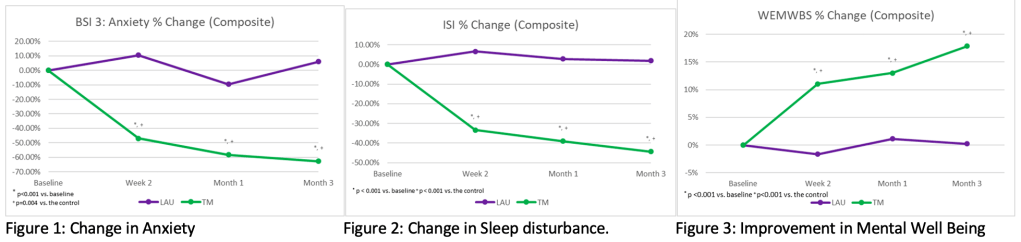
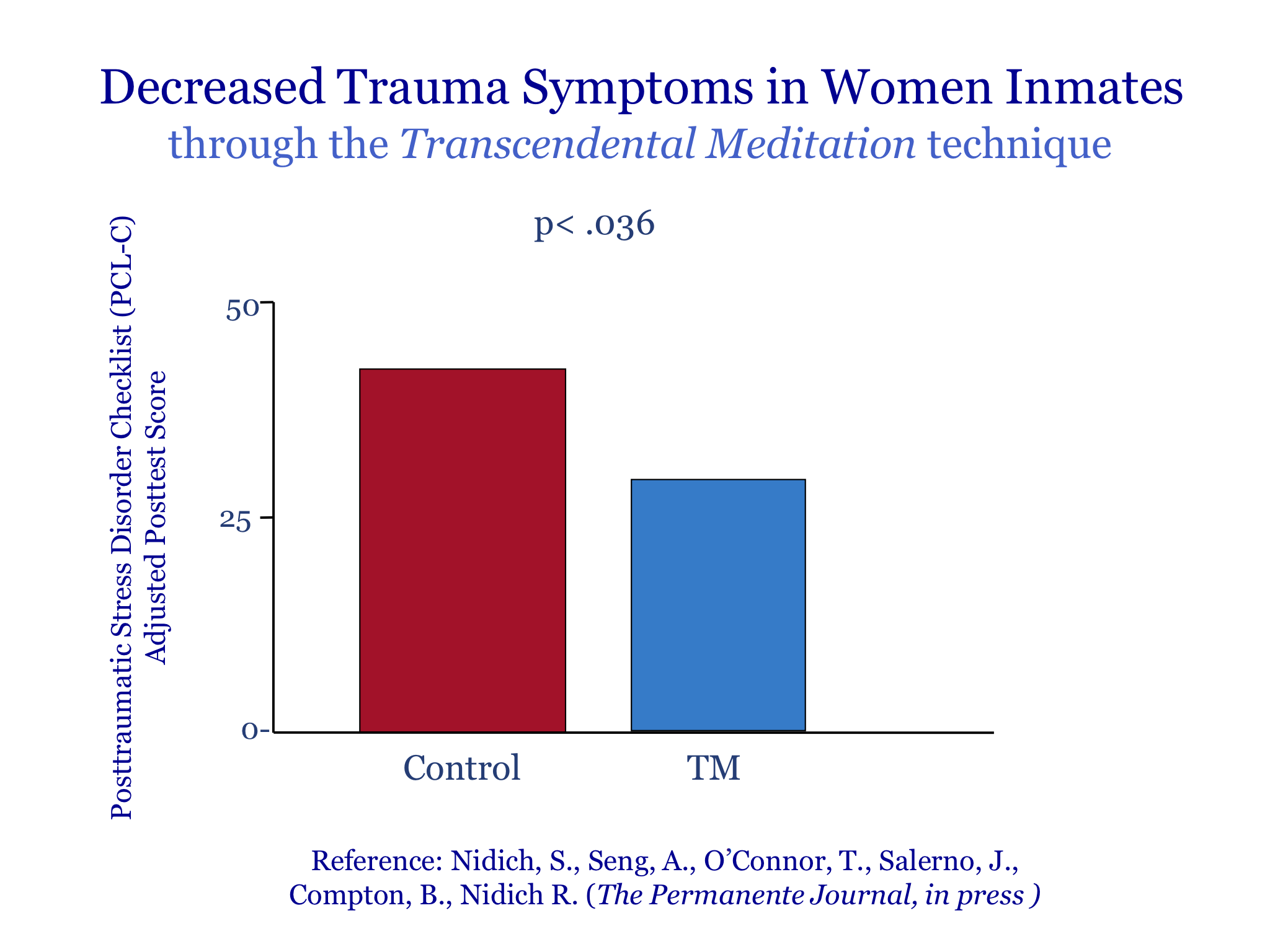
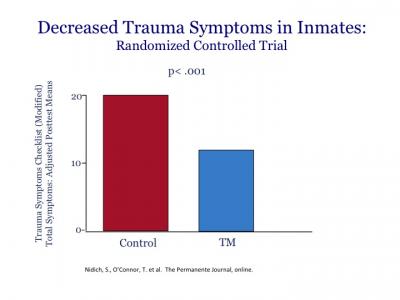
Today, I wanted to address you on the effects of Transcendental Meditation on PTSD, post-traumatic stress disorder, depression and sleep problems in veterans, military personnel, and other high risk groups. We’ll be covering a lot of the research that’s been published on this very specific and effective program of Transcendental Meditation that has been taught and researched around the world for over the past 4 to 5 decades. It’s something that millions of people have been practicing in the United States and around the world, that many, many people are practicing in Ukraine.
There’s some initial research that is ongoing right now in Ukraine dealing with mental health issues in women. And there are other projects, perhaps with the military there at early stages that are being planned with Transcendental Meditation.
For transparency purposes, I started Transcendental Meditation in my first year of college at George Washington University in Washington, DC. There was hardly any research at the time that I started several decades ago. And since that time, there’s been over 700 research studies alone on Transcendental Meditation and over 400 peer reviewed independent studies on Transcendental Meditation conducted around the world.
My name is Dr. Sanford Nidich. I’m the Director of the Center for Social Emotional Health and Consciousness Research, Director of the Dr. Tony Nader Institute for Research on Consciousness and Applied Technology, and Professor and the Director of the PhD program at Maharishi International University, the Program on Physiology and Health, particularly Maharishi AyurVeda, which is a traditional system of healthcare utilized by millions of people around the world.
Central to that natural system of medicine is the practice of Transcendental Meditation, which is easy to learn, systematically taught to people everywhere in the world in the same way. And it’s really been something that has been a life-changer for many, many people, from veterans and active military to prison inmates to healthcare providers. In terms of women’s health, in terms of the mental health and academic performance of college students and high school students, and in other specific areas of medicine medicine, such as cardiovascular disease, oncology, and other medical disciplines.
It’s been a program that researchers throughout the world have been researching, including very top researchers in the United States at Columbia University Medical School, University of Michigan Medical School, Georgetown University Medical School, and on and on, Howard University in Washington, DC, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, California.
So, it’s a practice that is easy to learn. Produces a unique state of restful alertness whereby during the 20 minutes of practice, the brainwave activity becomes more coherent and orderly, leading to greater executive functioning, memory, other cognitive factors. And at the same time that it’s producing a heightened state of alertness, it’s producing very, very deep rest throughout the whole physiology.
It produces a fourth major state of consciousness beyond waking, dreaming, and deep sleep called a state of restful alertness, or a hypo-metabolic state of wakefulness. Again, where the body noticeably feels and experiences, it exudes a very deep state of rest, while at the same time, we’re still fully alert. It’s not a state of hypnosis. It’s not some program that we just practice once a day, and, you know, and when we feel better, we don’t have to practice it.
We practice it twice a day for 20 minutes. And it’s a lifetime program that we can do once we learn it. And there are people who’ve been practicing Transcendental Meditation for well over 40 years now who have learned it in the 70s and 80s. And the reason they do it is because the human potential is enormous.
Consciousness is the new frontier of medicine. And we can expand consciousness. We can develop our own consciousness, which is the basis of our own thinking and behavior. We can produce greater orderliness and balance throughout the whole physiology, throughout the whole mind and body as a result of enlivening pure consciousness at the very basis of all thought and matter.
So there’s a lot to look forward to. It’s truly a new horizon. It’s causing a new paradigm shift where consciousness is seen to be primary, giving rise to all of our thinking and behavior in a very positive, orderly society, beneficial manner.
So what I’d like to do is, is take my time now to address you and go over some of the key scientific research on Transcendental Meditation. So let me see if I can share my screen so that you can be able to see my slides. So the title of my talk is, Effects of Transcendental Meditation on PTSD, depression, and sleep problems in various high risk populations, and I’ll be covering research principally in these areas.
Go to 9:15 in the video to see the 20-minute PPT containing slides of scientific research presented by Dr. Nidich.
— Written and compiled (citing sources) by Ken Chawkin for The Uncarved Blog.